There are six (6) kinds of aberrations which cause image defects
in binoculars.
They comprise Seidel's five aberrations ( 1)
spherical, 2) astigmatism, 3)
curvature of field, 4) coma and 5)
distortion), and 6) chromatic aberration.
ln line with its belief that brightness and image sharpness are
the hallmarks of quality in binoculars, Nikon strives hard
to reduce aberrations in its renowned optics.
The result : sharp images with a minimum of aberrations, the Nikon
way! |
|
|
 1) Spherical aberration
1) Spherical aberration
Spherical aberration is defined as any deviation from the light source ( " P " in the figure) along the optical axis at the focal point of paraxial rays ( " P' " in the figure ).
This kind of aberration causes a noticeable softness of the image.
|

|
|
 2) Astigmatism
2) Astigmatism
In this case, horizontal stripes appear in focus and vertical stripes
out of focus, or vice versa. Astigmatism is most noticeable in the periphery
of the image in wide field binoculars.
Some so-called wide field binoculars on the market feature no astigmatism
correction. Nikon's wide field of view binoculars provide clear,
crisp images right up to the edge of the view field.
|
|
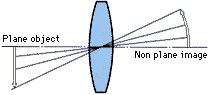
3) Curvature of field
 A plane object at right angles to the axis of an optical system does not appear as a plane image.
A plane object at right angles to the axis of an optical system does not appear as a plane image.
With binoculars affected by this aberration, you can focus around the center of the field, but the periphery of the field will appear out of focus, or vice versa.
Nikon's binoculars 7x50
and 10x70 IF SP WP for example, incorporate optical systems which
fully compensate for image curvature. These binoculars are particularly
well suited to astronomical observation.
|
|
|
 4) Coma (comatic aberration)
4) Coma (comatic aberration)
Coma aberration is manifested by an image with a comet-like extension.
As coma increases toward the exterior of the lens, it affects the periphery of the viewfield.
|
|
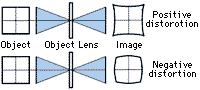
5) Distortion
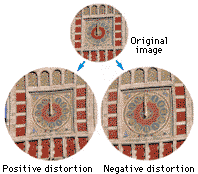 When the image differs geometrically from the object, you have distortion. There are two types of distortion : 1) positive and 2) negative, both caused by variations in the magnification.
When the image differs geometrically from the object, you have distortion. There are two types of distortion : 1) positive and 2) negative, both caused by variations in the magnification.
As distortion increases, although the image appears in focus over the
entire field, the size of the image differs at the center and peripnery
of the field of view.
|
|
|
6) Chromatic aberration
 Chromatic aberration is caused by a difference in light wavelength.
Chromatic aberration is caused by a difference in light wavelength.
The focal length (Fig. 1) or magnification (Fig. 2) of a lens varies
according to the wavelength of each type of incident light. Accordingly,
if you look at an image through a lens with chromatic aberration, the
image is blurred and appears colored at the fringes. In general,the
higher the magnification, the bigger the chromatic aberration.
Nikon has developed its own original ED
glass (Extra-low Dispersion) featuring minimized chromatic aberration.
Nikon' s ED glass fitted fieldscopes
produce clear, brilliant images with true colour.
|
| Note : |
The photographs are simulations for illustration purposes only
and not actual images. |
|
| |
Colour of photographs appearing in
this www site may differ from the originals.
Specifications and equipment are subject to change
without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer. |
| Nikon
Legal Information |
Privacy |
 2005
Nikon Vision Co., Ltd. 2005
Nikon Vision Co., Ltd. |
|